Concrete Scanning with GPR in 3D
Grid-based GPR scanning and 3D radar imaging for detailed as-built documentation of concrete structures
Concrete Scanning with GPR in 3D
Concrete scanning with GPR in 3D is a non-destructive evaluation method used to locate and visualize embedded features within concrete structures. Unlike traditional real-time scanning, 3D GPR scanning is performed using a formal grid pattern to generate detailed radar datasets that can be processed into depth slices and three-dimensional models.
This approach is commonly used when enhanced visualization, documentation, or as-built information is required for planning, verification, or condition assessment activities.
Concrete Structures Evaluated with 3D GPR
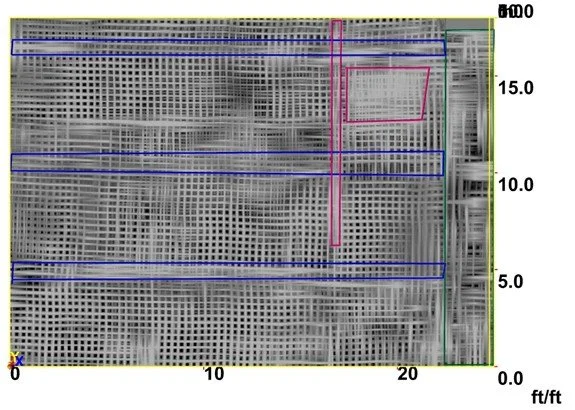
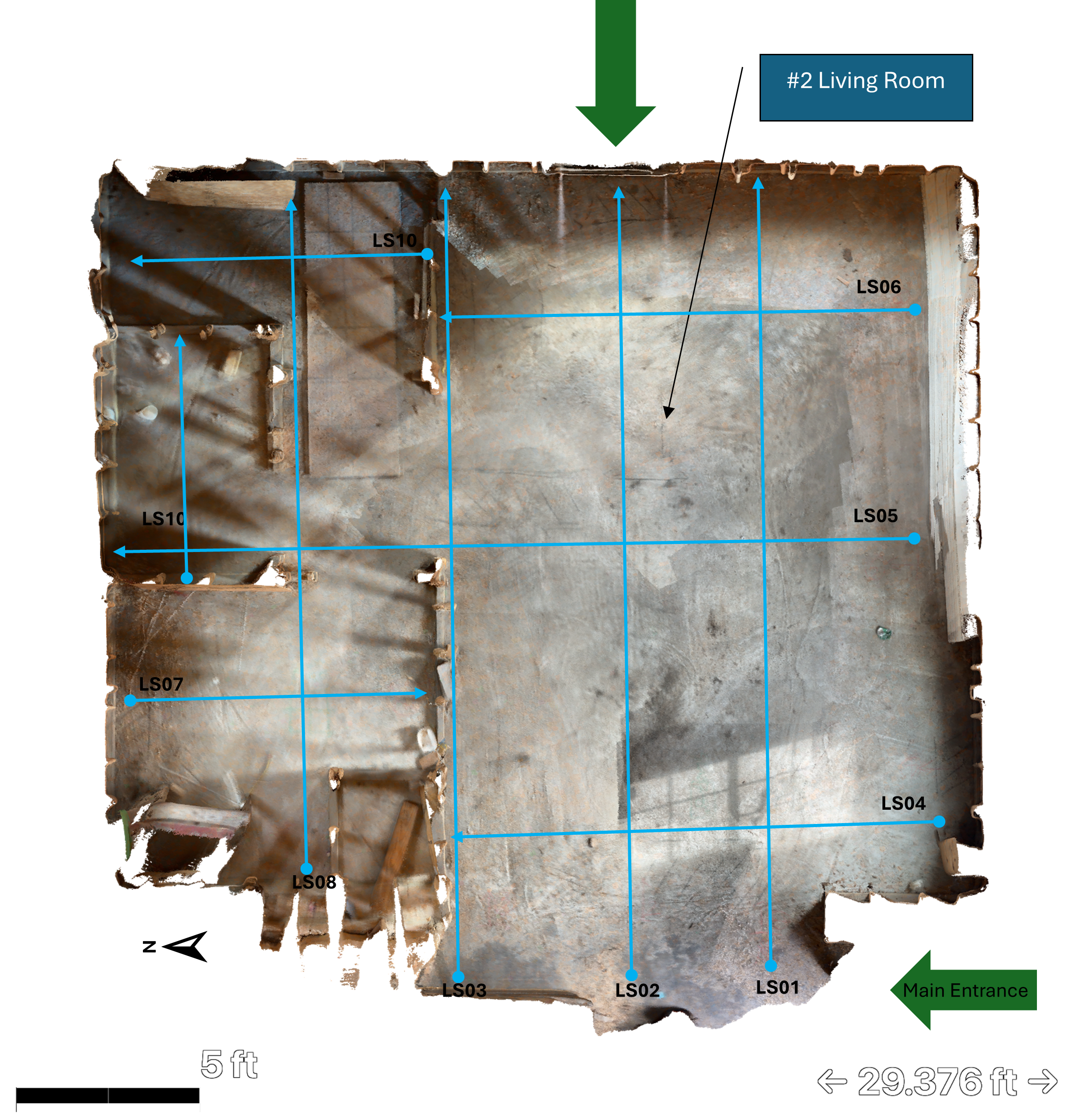
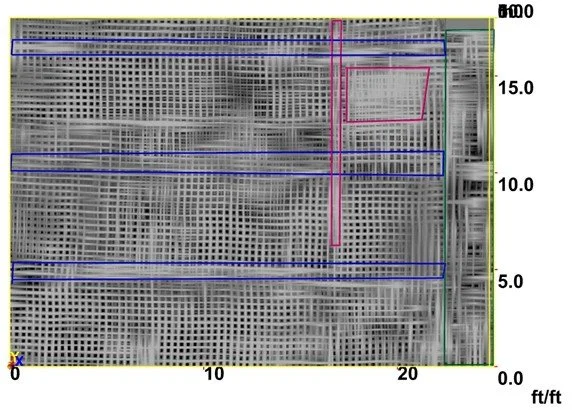
3D GPR scanning can be applied to a wide range of concrete elements, including concrete slabs, beams and girders, columns, CMU walls, and metal pan decking or composite slabs. By collecting data in a controlled grid pattern, reinforcement layouts and embedded features can be visualized more clearly than with single-direction line scans.
3D GPR Scanning Method
The concrete scanning process begins with defining the scope of work and assessing the scan location. Data acquisition is performed in 3D mode using high-frequency GPR antennas and a consistent grid layout to ensure adequate coverage and resolution. Scan line spacing is selected based on the structure type and required level of detail.
The collected radar data captures reflections from embedded reinforcement and material boundaries throughout the scanned area, allowing for detailed subsurface interpretation.
3D Radar Imaging and As-Built Information
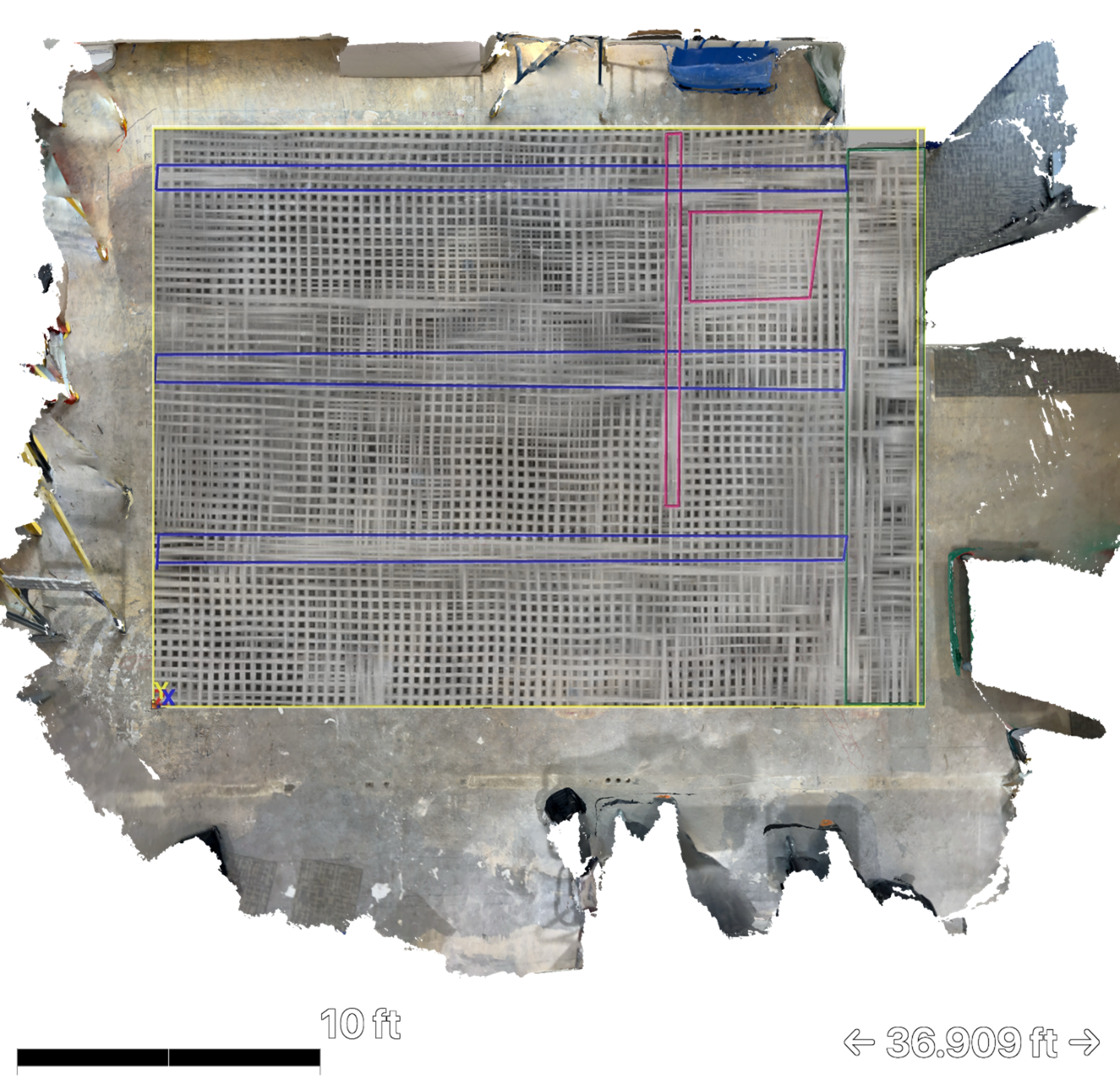
Following data acquisition, the GPR dataset is processed to support interpretation and visualization. This may include the creation of depth slices from the 3D radar dataset, generation of digital 3D models illustrating reinforcement layout, identification of post-tension cables, rebar patterns, and structural features, and production of as-built documentation for planning or verification.
These outputs provide a clearer understanding of subsurface conditions than surface markings alone and are commonly used to support retrofit work, coordination, and documentation needs.
Typical Applications of 3D GPR Scanning
3D concrete scanning is commonly used for as-built documentation of concrete structures, verification prior to cutting, drilling, or coring, structural condition assessments, coordination for renovation or retrofit projects, and enhanced visualization of reinforcement layouts.
Important Considerations
Ground penetrating radar is a non-destructive, interpretive technology, and results may vary depending on concrete composition, reinforcement density, and site conditions. 3D GPR scanning does not replace structural engineering evaluation, and final decisions regarding construction activities remain the responsibility of the project team.
Need Detailed As-Built Information for a Concrete Structure?
3D GPR scanning provides enhanced insight into embedded conditions without destructive testing.
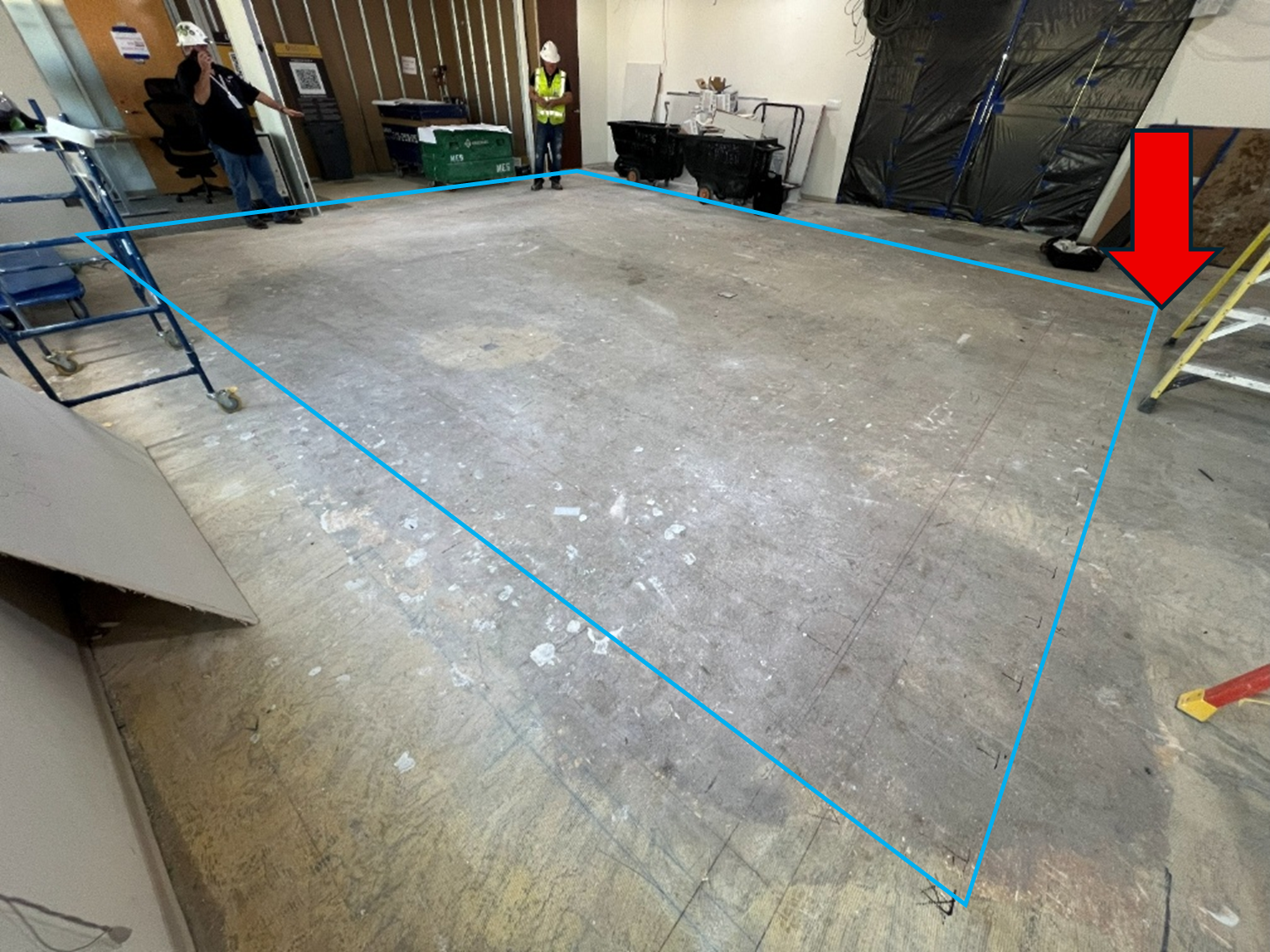
Elevated concrete slab marked for 3D GPR scanning to identify reinforcement and structural elements.
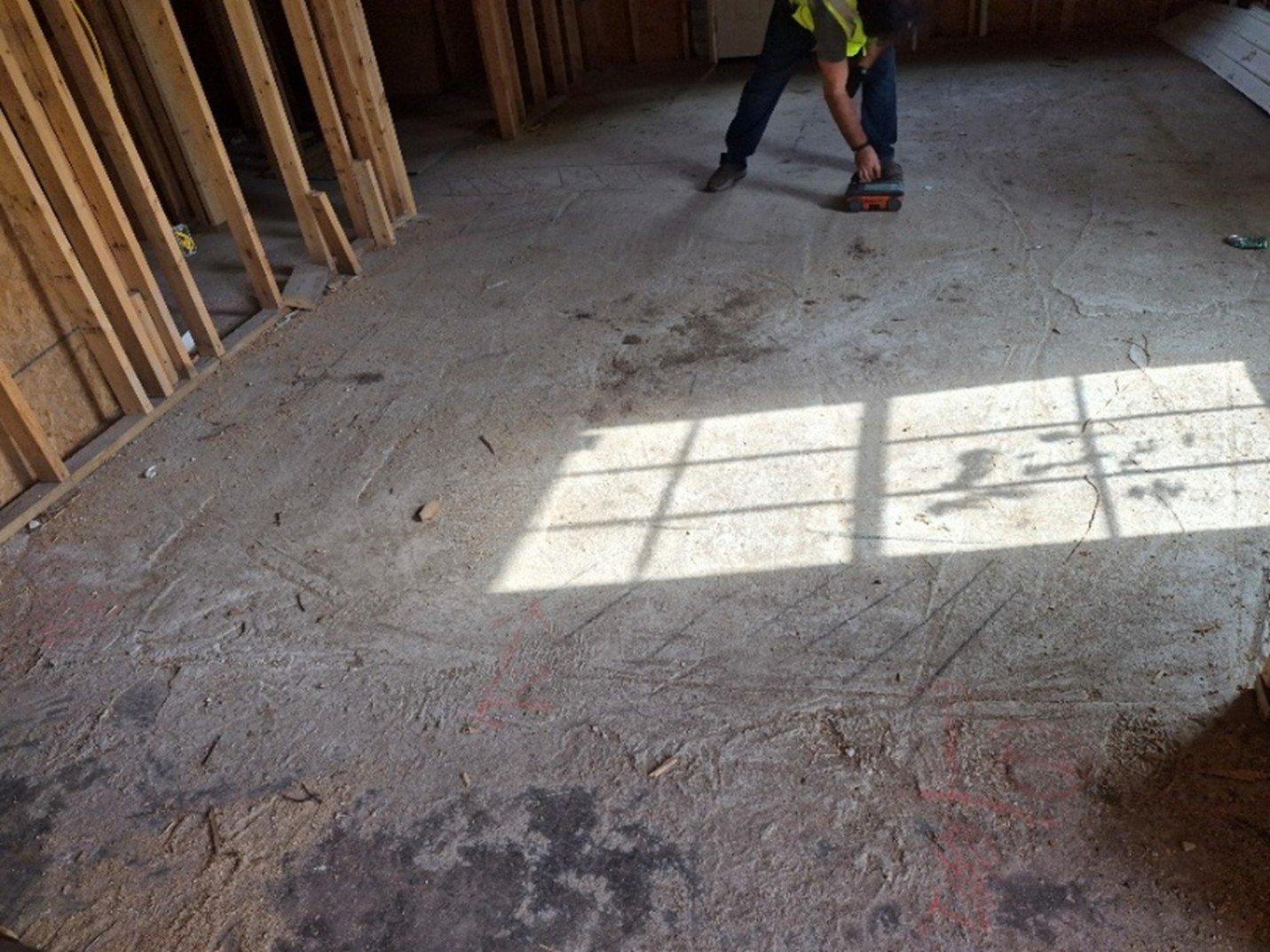
OmniVueNDT technician performing 3D GPR scan using systematic grid pattern on concrete floor.
3D radar time slice showing color-coded structural elements and reinforcement beneath concrete slab.
Complete 3D scan layout showing systematic grid coverage of residential floor plan.
Hybrid LiDAR and GPR visualization showing internal reinforcement mapped onto physical space.