Storage Tank Deformation Analysis with 3D Laser Scanning
High-accuracy geometric assessment of storage tank verticality, settlement, and structural deformation using 3D LiDAR technology
3D Laser Scanning for Tank Geometry & Settlement Assessment
Storage tank deformation analysis is performed to evaluate the geometric integrity, vertical alignment, and potential settlement of above-ground storage tanks. OmniVueNDT utilizes high-resolution 3D LiDAR (Laser Scanning) technology to capture precise spatial measurements of tank structures without physical contact or destructive testing.
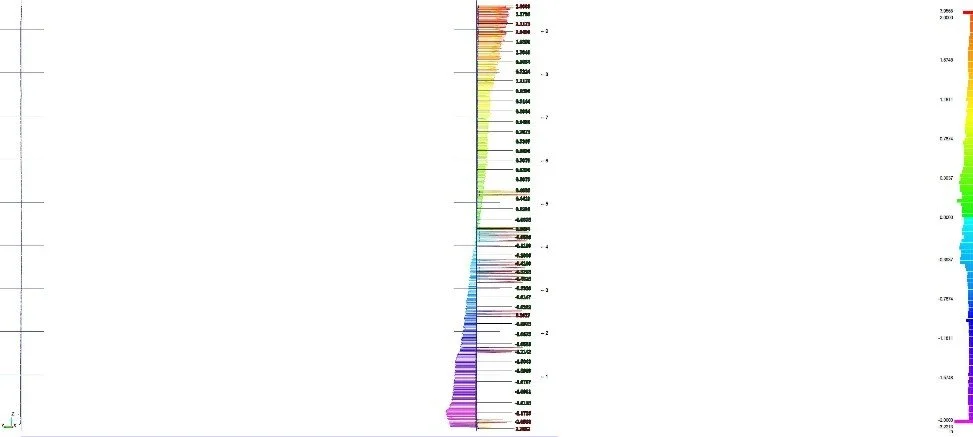
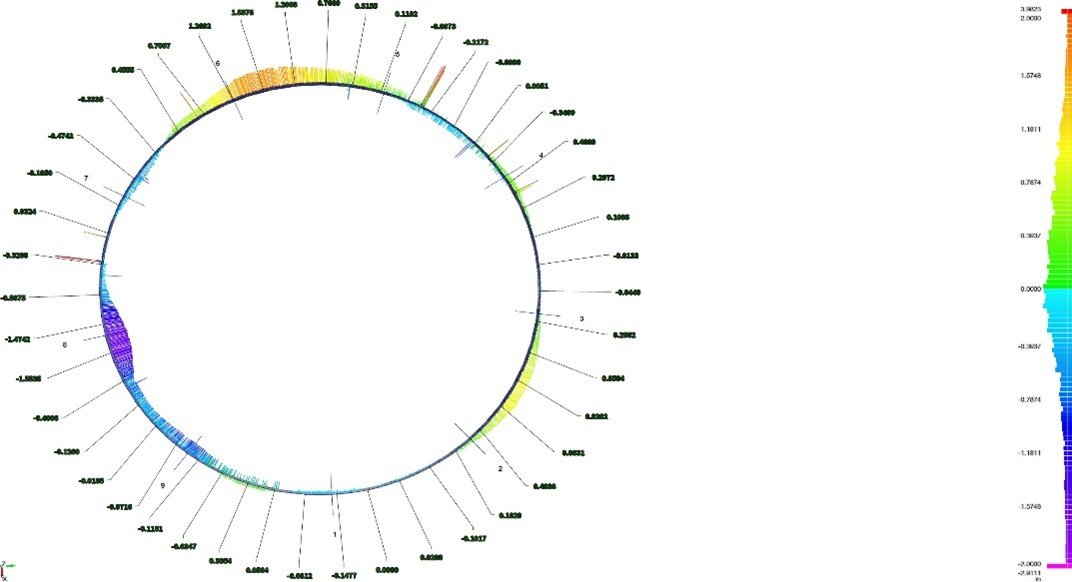
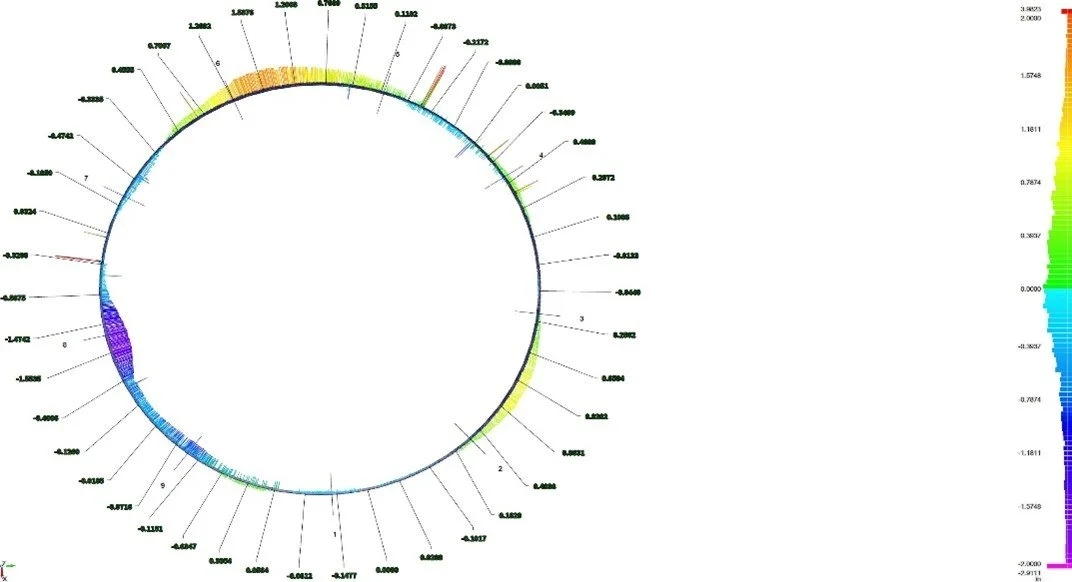
Unlike subsurface scanning methods, 3D laser scanning captures millions of spatial data points across the tank surface, creating a highly accurate digital representation of the structure. This point cloud dataset allows for detailed evaluation of verticality, roundness, settlement, bulging, and other deformation characteristics.
Laser-based tank assessment provides objective, measurable data to support engineering evaluation and maintenance planning.
3D LiDAR Data Acquisition & Processing
Laser scanning is conducted using high-precision terrestrial LiDAR systems positioned strategically around the tank perimeter. Multiple scans are registered together to create a unified 3D point cloud model representing the entire tank geometry.
The collected data is processed to:
Evaluate tank verticality and plumbness
Identify settlement patterns at the tank base
Detect shell deformation or bulging
Assess roundness and geometric tolerances
Generate cross-sections and deviation maps
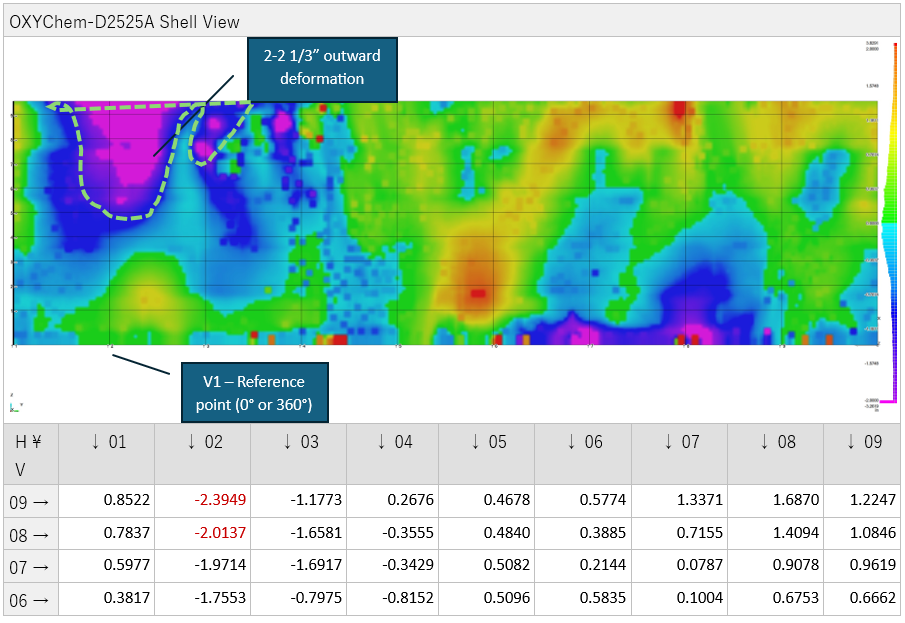
Color-coded deviation analysis may be used to visualize out-of-tolerance areas relative to a best-fit geometric model.
Typical Applications
3D laser scanning for storage tanks is commonly used for:
Verticality and plumbness verification
Settlement monitoring
Structural deformation assessment
Pre-maintenance evaluation
Engineering documentation
Condition assessment prior to repair or retrofit
This method provides accurate, repeatable measurements without requiring direct physical measurement or shutdown in many cases.Corrosion Mapping
Corrosion mapping is performed using half-cell potential testing, also known as NDT corrosion mapping. A grid is established around the affected or investigated area, typically with grid spacing of 4 to 6 inches, and data is collected at each grid point.
The collected data is processed into a numeric dataset and used to create contour maps that illustrate potential corrosion activity within the reinforced concrete. These maps help identify areas of concern and guide further investigation or repair planning.
Deliverables & Reporting
Following data collection and processing, OmniVueNDT provides:
Registered 3D point cloud models
Deviation and deformation maps
Cross-sectional analysis
Quantified verticality measurements
Engineering-ready data exports
These deliverables support informed decision-making for structural evaluation, maintenance planning, and regulatory documentation.
Important Considerations
3D laser scanning evaluates geometric conditions and surface deformation. It does not assess internal corrosion, material thickness, or subsurface reinforcement unless combined with other testing methods. Final engineering interpretation and structural capacity evaluation remain the responsibility of qualified engineering professionals.
Planning a Tank Deformation Assessment?
High-accuracy 3D laser scanning provides measurable insight into tank alignment, settlement, and structural geometry. Contact OmniVueNDT to schedule a deformation analysis and support informed engineering evaluation.
Advanced structural analysis showing condition assessment results with color-coded visualization.
Cross-section analysis showing structural deviations and areas requiring detailed evaluation.
Comprehensive condition map with quantitative measurements for engineering assessment and repair planning.